Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high dblood sugar, either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced. There are several types of diabetes, the classification being related to the mechanisms through which the disease develops. The main types are: Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin or the cells ignore the insulin (they no longer respond adequately to normal levels of insulin). People can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, but this type of diabetes is most often associated with older age. Type 2 diabetes is also associated with excess weight, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, previous history of gestational diabetes, and certain ethnic groups.
Pre-diabetes is when blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. Pre-diabetes means a person is at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes, as well as for heart disease and stroke. Many people with pre-diabetes develop type 2 diabetes within 10 years. However, weight loss and moderate physical activity can help people with pre-diabetes delay or prevent type 2 diabetes.
Diagnosis of Diabetes
Diabetes is diagnosed based on symptoms and blood sugar tests. The following tests are used to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes:
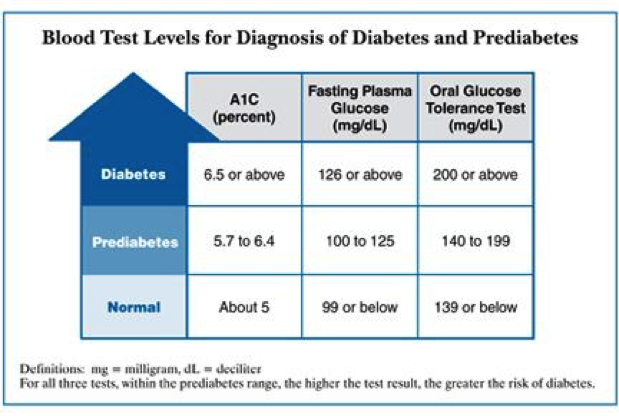
- A fasting blood glucose level of over 126 mg/dl (7 mmol/l)
- If glucose level is higher than 200 mg/dL after 2 hours of drinking a glucose drink (called oral glucose tolerance test; OGTT)
- A level of glycated hemoglobin (Hemoglobin A1c) of over 6.5%. See A1C test.
- A random plasma glucose (RPG) higher than 200mg/dL, in a patient with classic symptoms
Diagnosis of Diabetes and Prediabetes, National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst and fluid intake
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Increased hunger
- Sores that do not heal
Complications of Diabetes
Constantly elevated levels of sugar in the blood are toxic for most organs due to the damage they cause to blood vessels and nerves. If these vessels cannot provide adequate blood flow, most organs in the body cannot get nutrients and oxygen and become dysfunctional. Diabetes can potentially damage any organ system. Thus, diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to complications over time. The longer you have diabetes, and the less controlled your blood sugar is, the more likely you are to develop the following:
- Diabetic retinopathy – eyesight problems due to diabetes. After 20 years of poorly controlled diabetes more than 75% of patients can develop this complication.
- Diabetic nephropathy – kidney problems due to diabetes. The body loses protein in the urine, and blood pressure is increased. Diabetic nephropathy usually develops after about 15 years of poorly controlled diabetes.
- Diabetic neuropathy – nerve damage due to diabetes. Nerve damage is commonly manifested through pain followed by loss of feeling in the affected areas of the body (usually the legs). Patients can lose all sensation in their legs potentially leading to severe injuries.
- Peripheral vascular disease – Arteries that supply the arms or legs can become damaged leading to impaired blood flow. Diabetic patients often have leg pain when walking (also called ‘intermittent claudication’).
- Cardiovascular disease – Diabetes also affects the blood vessels supplying cardinal organs, such as the heart and brain, thereby increasing the risk for heart attacks and strokes.
- Infections – Diabetic patients have an increased risk of infection, since high blood sugar levels provide a medium in which bacteria can thrive. The immune system is also less effective in diabetes.
- Lower limb injuries – Since sensation in the feet is decreased due to diabetic neuropathy, injuries are not felt and can become severe and infected. Such injuries heal very slowly in diabetics. Deep infections and low blood flow may result in the need to have fingers, toes, or other body parts removed (amputated).
Many of these complications produce no symptoms in early stages, but most can be prevented with a combination of regular medical care and blood sugar monitoring.
Treatment of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease that requires lifetime treatment. Treatment focuses on keeping blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible. This is accomplished with diet, exercise, and use of appropriate medications. Complications of diabetes are far less common and less severe in people who have near-normal blood sugar levels. Attention is also paid to other health problems that may accelerate the effects of diabetes, such as smoking, elevated cholesterol levels, obesity, and high blood pressure.
Consider the following points for optimal diabetes care:
- Make healthy food choices; eat foods that have less fat and salt, and more fiber.
- Get 30 minutes of physical activity on most days of the week.
- Stay at a healthy weight by sticking to your meal plan and being more physically active
- Check and record your blood sugar levels regularly. Be sure to take this record to your doctor visits.
- Talk with your doctor about individualized blood glucose targets. Ask how and when to test your blood glucose and how to use the results to manage your diabetes.
- Take your prescribed medicine even when you feel good.
- Control other medical conditions that increase your risk of cardiovascular disease, such as high blood pressure or cholesterol.
- Stop smoking. Ask for help to quit.
- Check your feet every day for cuts or sores. Contact your doctor if sores do no heal.
- Report any changes in your eyesight to your doctor. Visit a specialist for an eye-exam every year.
- Learn to cope with stress. Stress can raise your blood sugar, and while it is hard to remove stress from your life, you can learn to better handle it.