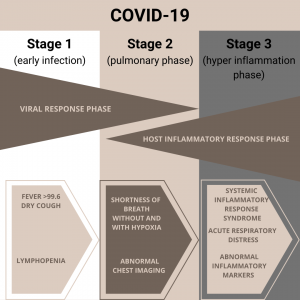
One of the causes of death for those infected with the coronavirus (COVID-19) is an immunological phenomenon. As you can see from the image below, this occurs in phase 3.
A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multi-center clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of Ruxolitinib in patients with COVID-19 cytokine storm started March 31 and should be completed late October.
This phase 3 trial is the result of a researcher from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, Gary Huang, recognizing a similarity of a rare children’s disease hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with the cytokine storm of COVID-19. He contacted his colleague, Janfeng Zhou, MD, PhD in Wuhan China and they conducted a phase 2 clinical trial with 43 patients, 21 were control receiving standard of care treatment. At day 14, the CT scans of 90% of patients receiving the Ruxolitnib were significantly improved compared to only 9% of the control group. None of the patients receiving Ruxolitnib died.[2]
In another study, the Recovery Trial, going on in the United Kingdom, hospitalized patients who were on oxygen or on ventilators were treated with Dexamethasone. Dexamethasone is an anti-inflammatory drug and it was found to reduce deaths by one-third for those patients on ventilators and by one-fifth for patients on oxygen.[3]
Until a vaccine is ready for use, it is good to see that treatments are being identified for use.
References:
- Siddiqi H, Mehra M. (2020). COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical–therapeutic staging proposal. Jounal of Heart and Lung Transplant, 39(5): 405–407. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012
- Cao Y, et.al. (2020).Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.019
- Horby P, et.al. (2020). Effect of Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Preliminary Report https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.22.20137273v1